Adaptive Frame Rate for Egocentric Video
 System Overview
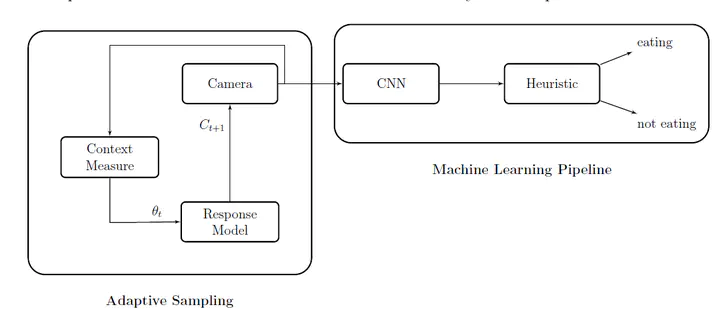
System Overview
The goal of the project seminar is to implement an adaptive sampling strategy to dynamically tune the sampling rate of a wearable egocentric camera. The sampling rate will be tuned based on context measure, i.e., a measure of motion, extracted from the frames.
The increasing development new media and data acquisition techniques have lead to new innovative video recording set ups. A clear example of that is the egocentric video, where a camera on head or on the chest approximates the visual field of the camera wearer. This new camera setting offers a valuable perspective to understand user’s activities and their context. In this case, the wearable head-mounted egocentric camera set up pursued a dietary event spotting in a free living condition.
A main feature of free-living data is a long recording duration. However, this kind of camera often acquire irrelevant data for the analysis task. In this work we introduce an adaptive sampling strategy to dynamically tune the sam- pling rate of a wearable egocentric camera. The adaptive sampling rate is based on a context measure. It is a motion measure, indicative if the recorded activity might be of our interest.
To evaluate the sampling strategy we implemented a computational simulation of resource consumption in terms of energy consumption and memory storage. For this purpose, I designed an analytical energy and memory model, a nd base our analysis on data extracted from datasheets. Our energy and memory model considers both sensing components, i.e., the cmos sensor, and processing, i.e., the microcontroller to process the deep neural network.
The clear advantage of an adaptive frame rate is saving energy as the camera will not be acquiring data continuously. Benefits from our method will be longer recording sessions, smaller battery employment or smaller storage space usage. This would help to overcome the limitations of the video recording, in terms of power consumption, while maintaining acceptable performance. Furthermore, less data acquisition will also mean an energy saving in processing.